Why Prompt Engineering Is Your New Super Power as a Business Consultant
This is the first post in a series on practical prompt engineering for Business Central consultants and developers. Each post will build on the last, guiding you from the basics to advanced techniques for real-world productivity.
Coming up next:
- Blog Post 2: Laying the Groundwork - Understanding Input and Output Formats for LLM Success How to define output formats, provide context, use templates, personas, and few-shot prompting for better results.
- Blog Post 3: The Power of Templates - Using Meta Prompting to Create Effective Prompts for Recurring Tasks Leverage LLMs to help you create and refine prompts, including prompt generators and meta-expert techniques.
- Blog Post 4: Ace Your Interviews - Prompting for Effective Customer Interaction Preparation Use prompts to prepare for customer interviews, generate questions, and anticipate pain points.
- Blog Post 5: Clarity is Key - Using LLMs to Write Effective Feature Requirements Prompt for clear, structured requirements and iterate for precision.
- Blog Post 6: Code Smarter, Not Harder - Leveraging LLMs for Efficient Code Writing Prompt for AL code, code snippets, and structure for Business Central development.
- Blog Post 7: Debugging with AI - Getting Intelligent Assistance for Your Business Central Code Prompt LLMs to analyse, explain, and help debug your code.
🤖 AI is here—but it needs directions
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming the way we work in Business Central and beyond. But while AI tools like Copilot are powerful, they’re not mind readers. The real magic happens when you know how to communicate with them effectively. As a business consultant or developer, your ability to guide AI with the right instructions—known as prompt engineering—can make the difference between generic, unhelpful output and solutions that truly move your projects forward.
Prompt engineering is the craft of writing clear, context-rich instructions so an AI responds with maximum usefulness. Nail it and you ship features faster, capture cleaner requirements, and debug in minutes instead of days. Fumble it and you’ll waste time untangling vague, generic answers.
- 🤖 AI is here—but it needs directions
- ✍️ Prompt engineering in a nutshell
- 🛠️ Why this matters for Business Central professionals
- 💡 Mini case study—requirement-gathering chatbot
- ⚠️ Common pitfalls to dodge
- ✅ Rapid-fire prompt checklist
- 🧑🏫 Meta-prompting—let the AI teach you
- 🧩 Putting it all together
- 🔮 Looking ahead
✍️ Prompt engineering in a nutshell
Before diving into techniques, let’s clarify what prompt engineering is and why it matters.
Definition: The art and science of phrasing precise, contextual instructions that coax the best response from an AI model.
Think of it as the bridge between your business expertise and the AI’s capabilities. The better your prompt, the better the AI output—and the better your Business Central solution. That flow is your new edge.
🛠️ Why this matters for Business Central professionals
As a Business Central consultant or developer, you’re already juggling complex tasks like gathering requirements, writing feature requests, coding, and debugging. Mastering prompt engineering can make these tasks faster and more effective. Imagine:
- Customer interviews: Use AI to generate insightful questions and anticipate pain points.
- Feature requests: Prompt for clear, structured requirements that reduce miscommunication.
- Coding: Generate AL code snippets or debug faster with AI assistance.
- Debugging: Get intelligent explanations and solutions for tricky issues.
By learning to craft better prompts, you’ll unlock AI’s full potential and become more productive in your day-to-day work.
💡 Mini case study—requirement-gathering chatbot
| Prompt | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Vague “Ask the client about inventory requirements.” |
Bot fires one bland question. Zero depth. |
| Engineered “Act as a Business Central consultant gathering requirements for a retail inventory module. Greet the client, then ask (1) how they track in-store vs. online stock, (2) pain points in restocking, (3) must-have reports. Acknowledge each answer, drill deeper, end with a summary.” |
Structured interview yields rich insights and an instant summary. |
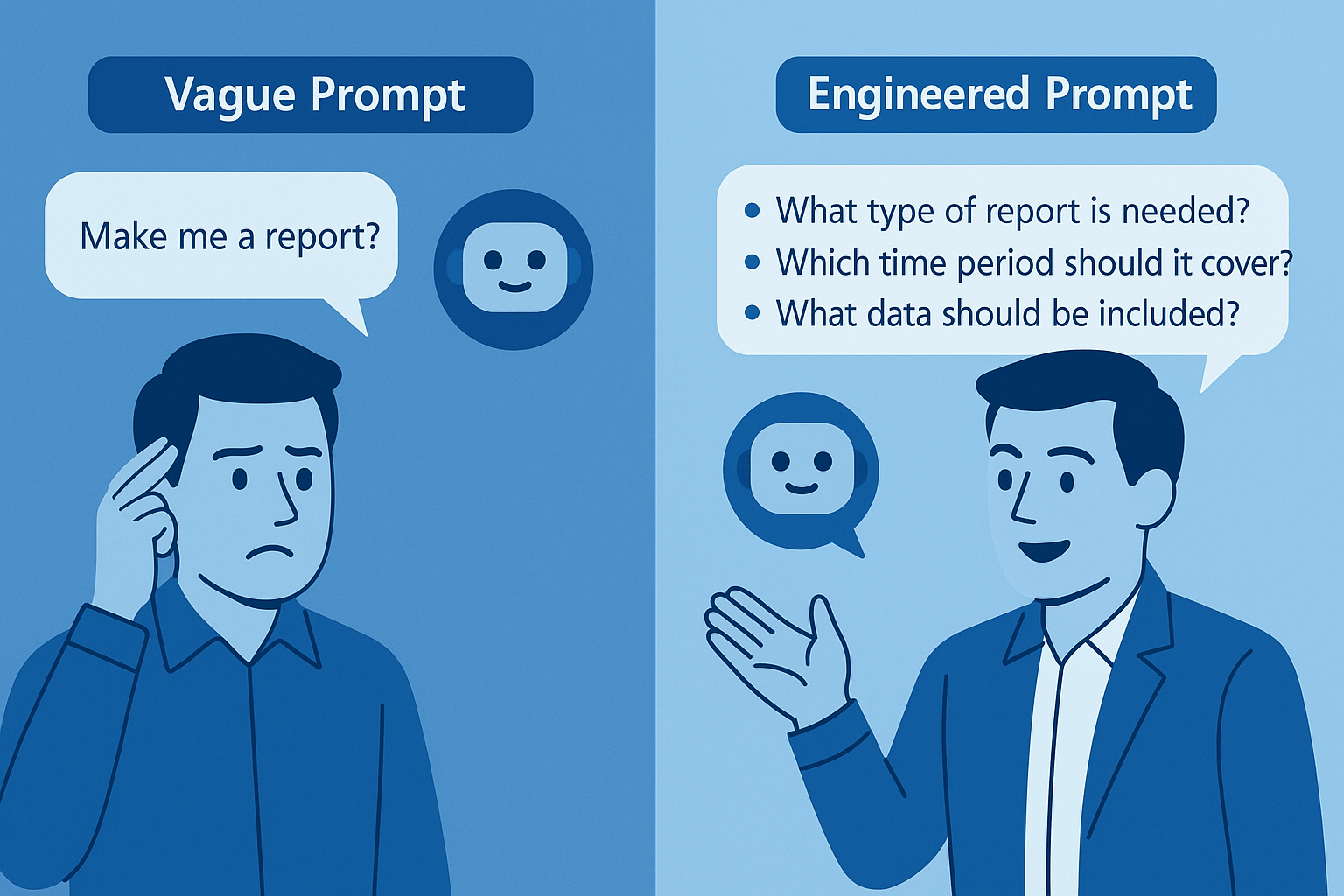
Lesson: Context + structure = transformative results.
Vague vs. Engineered Prompts: Pros and Cons
| Type of Prompt | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Vague | Quick to write May work for simple asks |
Often yields generic or incomplete answers Misses context Requires more follow-up |
| Engineered | Produces tailored, actionable output Captures business context Reduces back-and-forth |
Takes more time and thought to craft Requires understanding of both AI and business needs |
⚠️ Common pitfalls to dodge
As you start applying prompt engineering, watch out for these common mistakes:
- Treating complex asks as Google searches – “Configure approvals” is too thin for BC’s nuances.
- Skipping BC context – Without “Business Central v24, Finance module” you’ll get generic ERP answers.
- Kitchen-sink prompts – Five unrelated requests in one sentence confuse the model.
- No iteration – You will refine; plan on two or three cycles instead of blaming the AI.
✅ Rapid-fire prompt checklist
Here’s a quick checklist to help you craft better prompts every time:
- Start with the goal: “Generate AL that …” or “Summarise client pain points …”.
- Inject BC context: version, module, industry.
- Give structure: bullet points, numbered steps, requested format.
- Iterate: review the draft, tighten the prompt, rerun.
- Meta-prompt: when stuck, ask the AI how to improve the prompt.
Prompt Engineering as a Consultant Skill: Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Accelerates solution delivery | Requires practice and iteration |
| Improves requirements gathering | Can be time-consuming at first |
| Reduces miscommunication | Not a substitute for domain expertise |
| Makes AI output more reliable | May need to keep up with evolving AI models |
🧑🏫 Meta-prompting—let the AI teach you
If you’re unsure how to improve your prompt, ask the AI itself for help:
You: Improve this prompt for a BC warehouse scenario: “Explain item tracking.” AI: Try: “In Business Central v24, explain Lot vs. Serial tracking for a wholesale + e-commerce warehouse, covering setup, transaction flow, and best practices.”
You just turned the AI into your prompt editor.
🧩 Putting it all together
Let’s recap with a step-by-step approach you can use right away:
- Frame the ask in one sentence: “Generate AL code for …”
- Feed context: BC version, module, industry quirks.
- Specify form: table, JSON, bullet list, 50-word summary—whatever helps.
- Run it, review critically, iterate.
- Meta-prompt if you hit a wall.
Each iteration sharpens both the prompt and your mental model of what the AI can do. Soon you’ll feel like you’re pair-programming with a tireless expert—provided you tell it exactly what you need.
🔮 Looking ahead
Prompt engineering isn’t a one-off trick; it’s a habit that compounds. Master it now and you’ll:
- Slash development and debugging time.
- Capture requirements with zero “lost in translation.”
- Deliver cleaner, faster BC solutions that delight clients.
Next in this series: Input & Output Formats—patterns (tables, JSON, pseudo-code) that make AI replies plug directly into your BC workflow.
Happy prompting!